Transforming Manufacturing Productivity
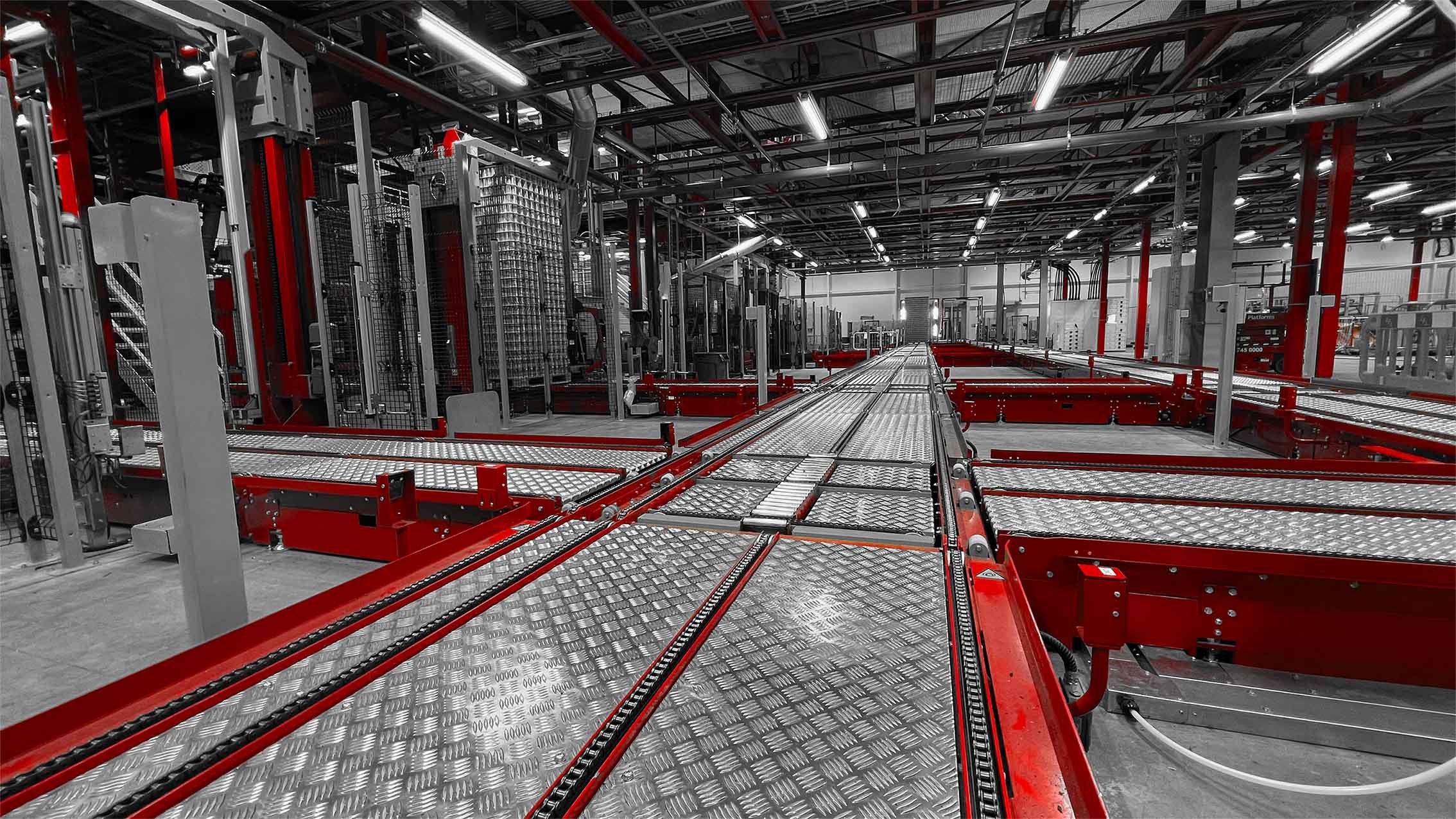
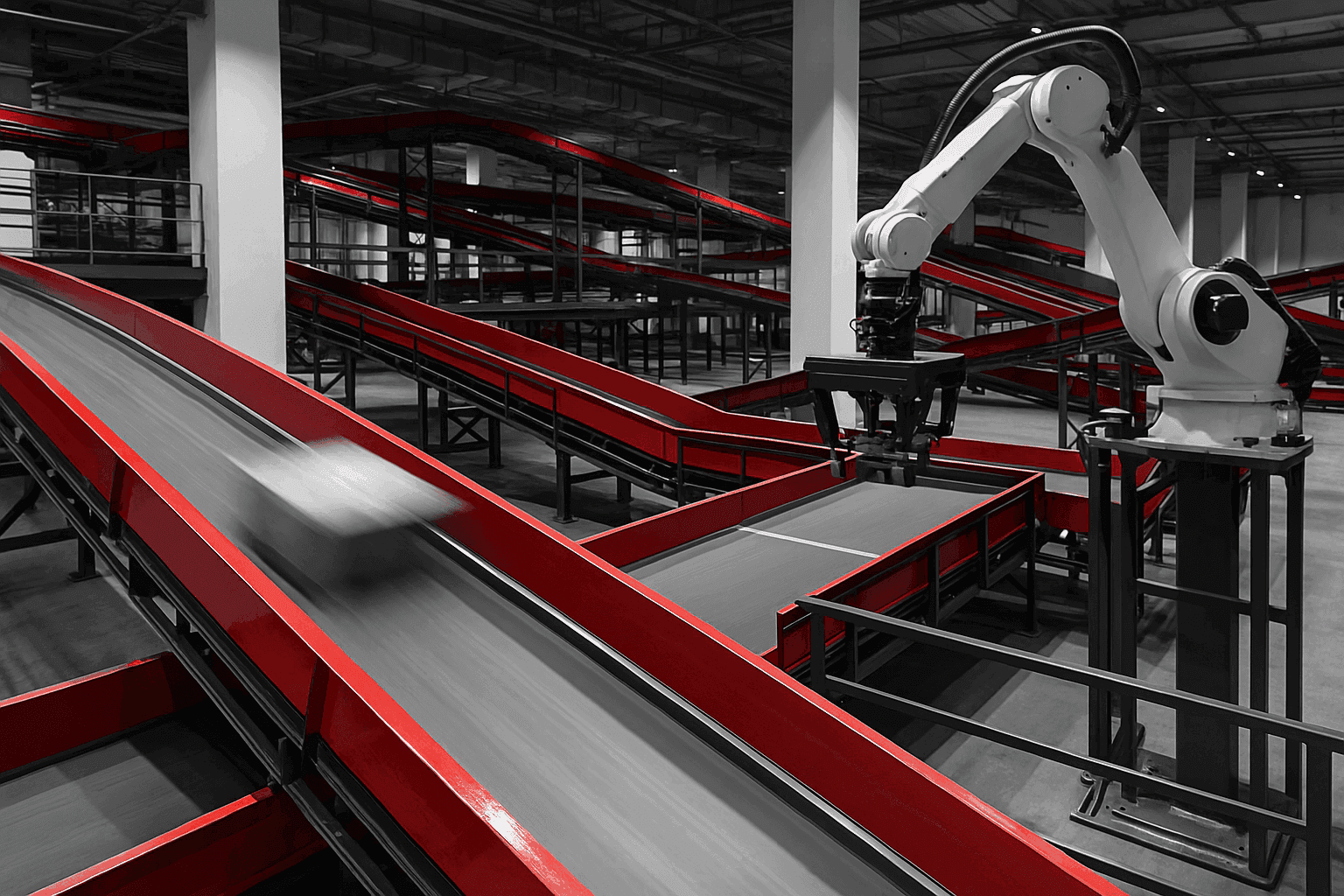
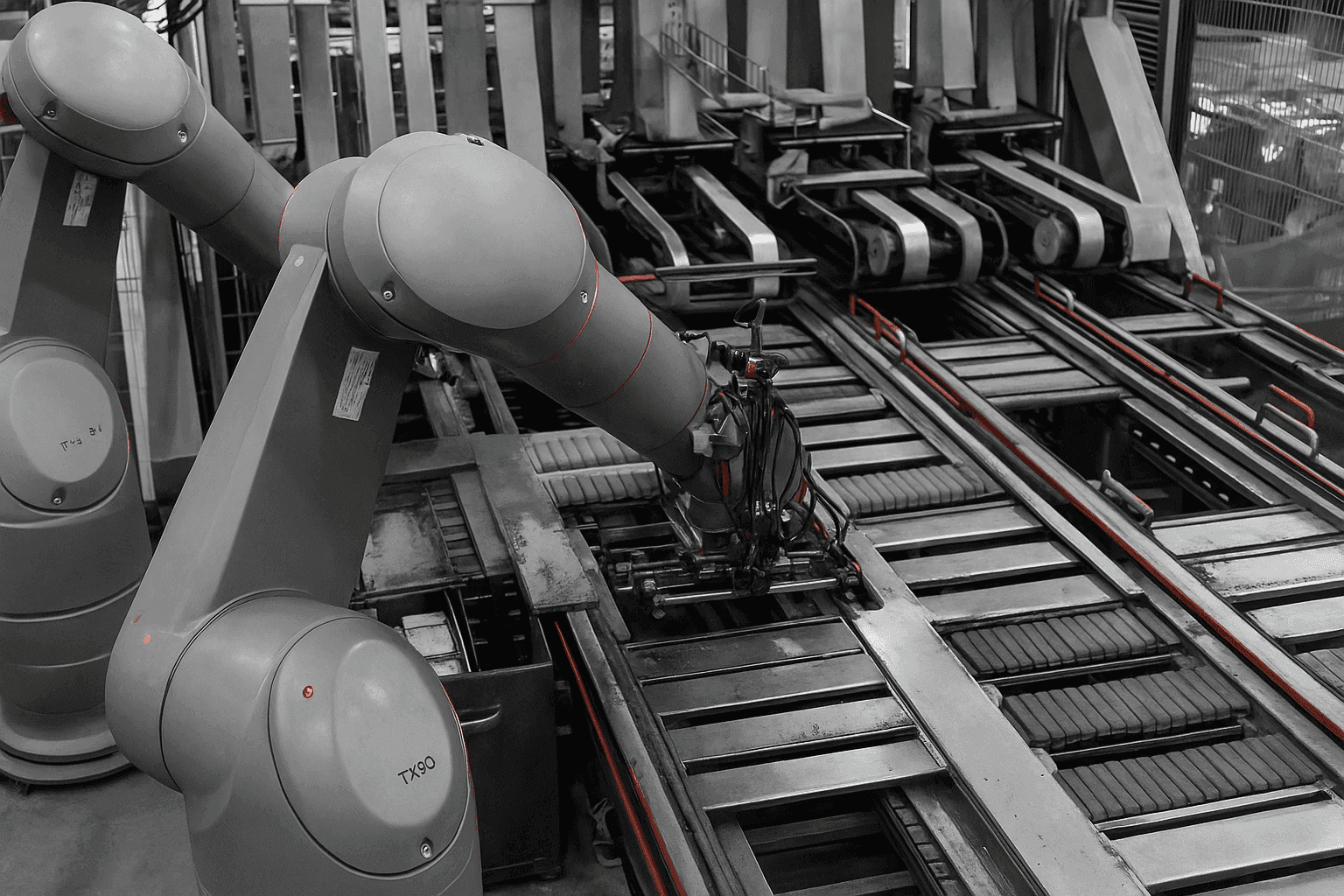
Cobots in the manufacturing industry are proving their worth across diverse applications. Assembly lines benefit from their precision in tasks such as pick-and-place operations, vision-guided quality inspections, and component fitting. In machine tending, cobots can load and unload CNC machines, presses, and injection moulding equipment, maintaining consistent operation during shift changes and breaks.
The automotive manufacturing sector has embraced cobots for tasks including screw driving, polishing, and parts testing. Electronics manufacturers deploy them for delicate assembly work that requires both precision and adaptability. Even smaller operations, previously unable to justify the investment in traditional automation, are finding prominent cobots economically viable due to their lower installation costs and minimal infrastructure requirements.