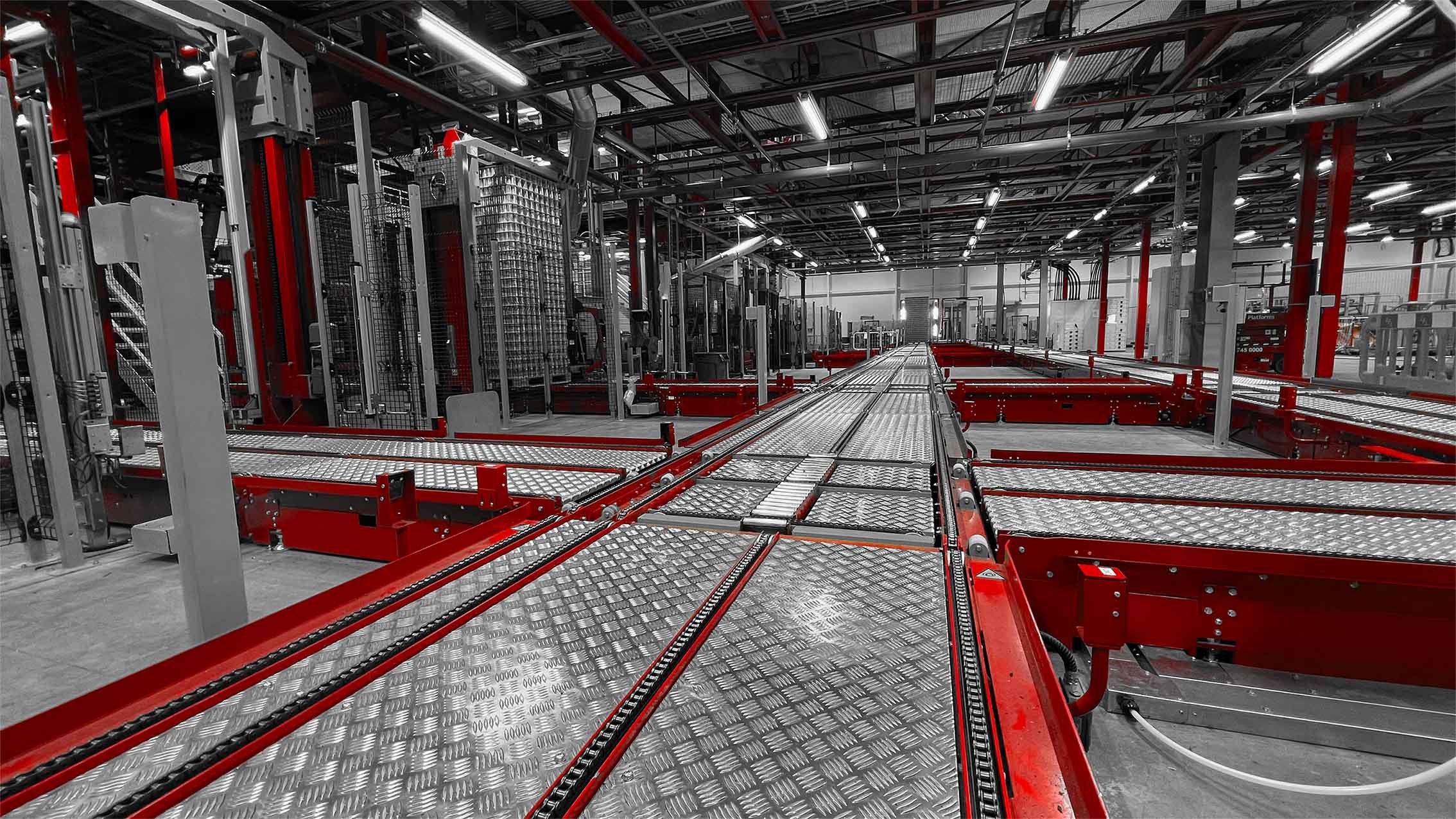
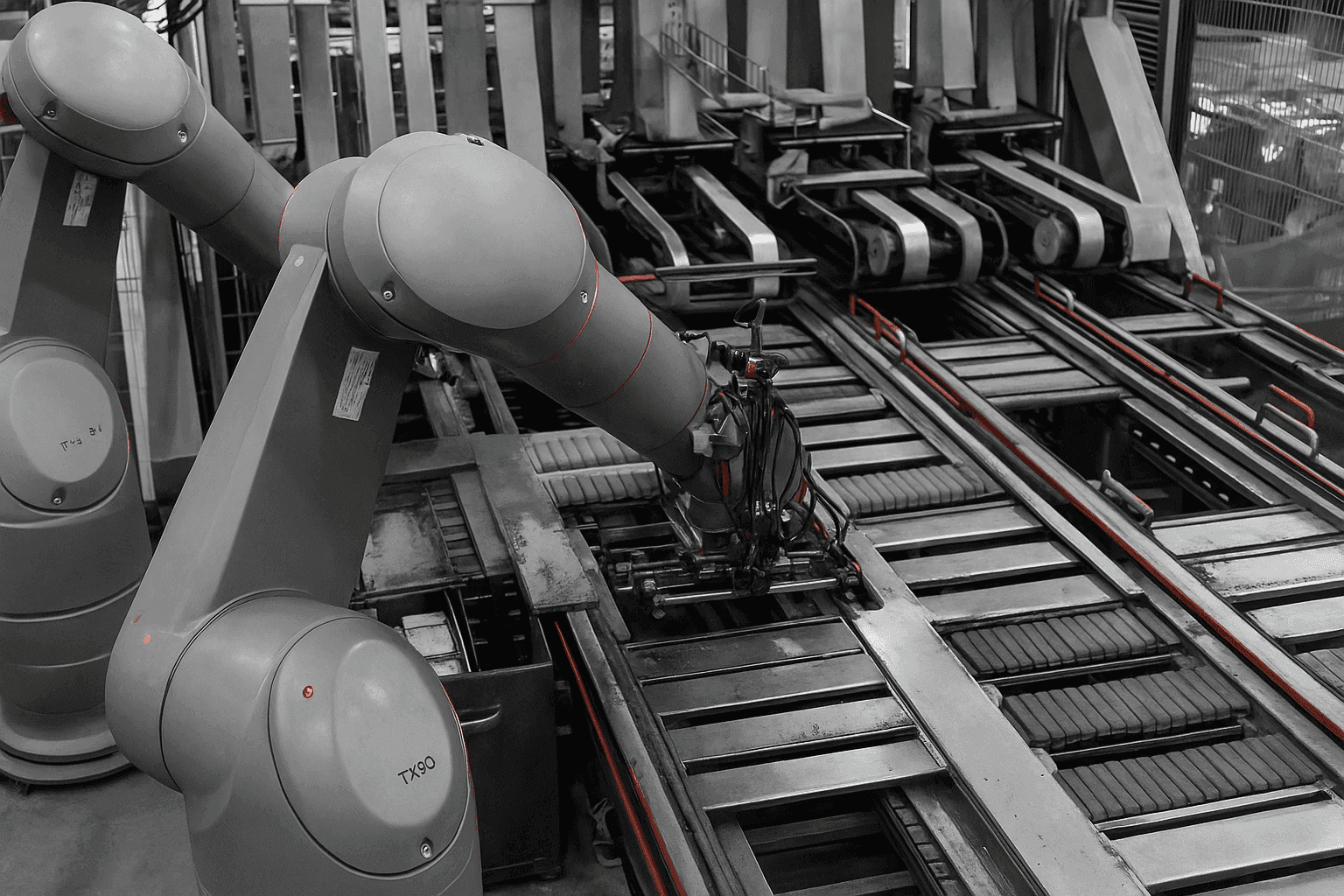
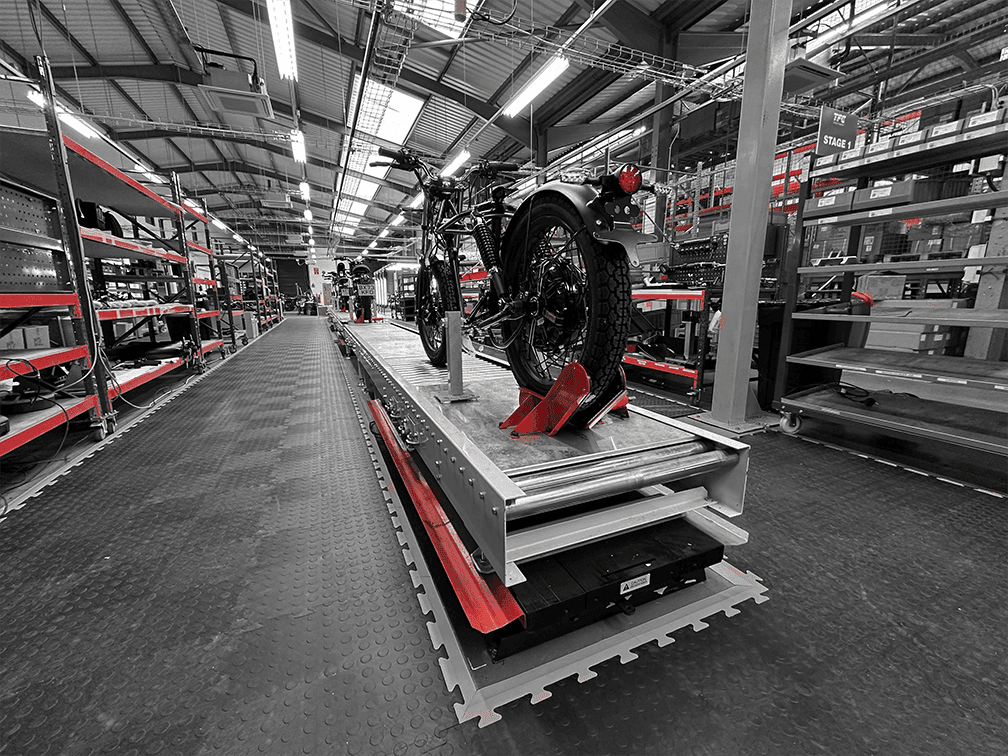
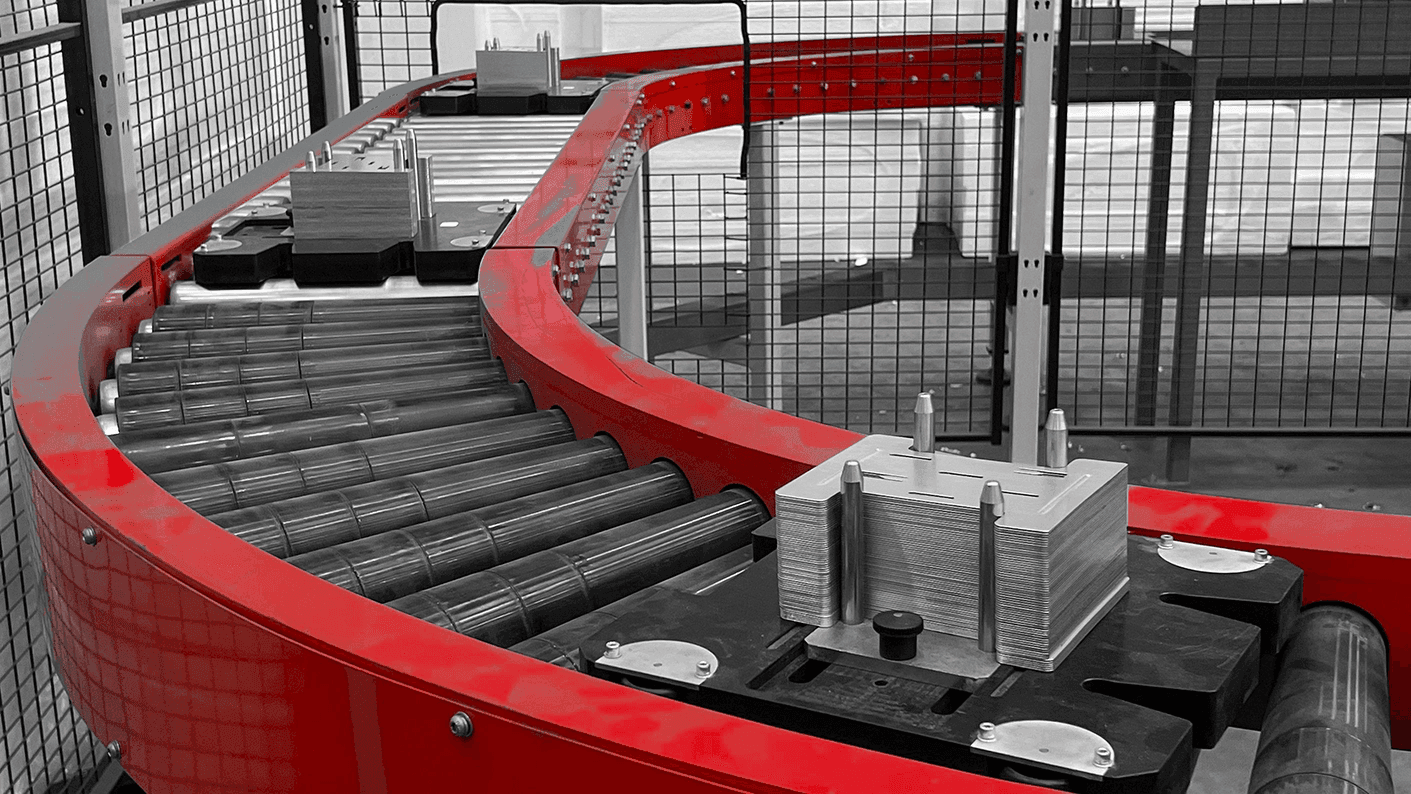
Flat Belt Conveyors
Before exploring advanced designs, it’s worth noting that flat belt systems form the foundation of most industrial conveyor solutions. These flat belt counterparts offer simplicity, versatility, and smooth material transfer for a wide range of industries. Flat belt conveyors represent the most common and versatile category of conveyor systems. These belts feature a smooth, level surface ideal for transporting lightweight to medium-weight items across horizontal or slightly inclined paths. Their simplicity makes them particularly popular in packaging facilities, assembly lines, and distribution centres. The construction of flat belts varies considerably depending on the intended application.
Materials range from PVC and polyurethane to rubber compounds, each offering distinct advantages in terms of durability, friction, and resistance to environmental factors. Food products and hygienic environments often require food-grade materials that meet strict hygiene standards and resist bacterial growth. Flat belts excel in applications requiring gentle handling of products, such as electronics assembly or pharmaceutical packaging. Their smooth surface minimises product damage whilst maintaining consistent transport speeds. Additionally, these belts can be easily configured with accessories like side guides, cleats, and belt tracking systems to enhance functionality.